Research
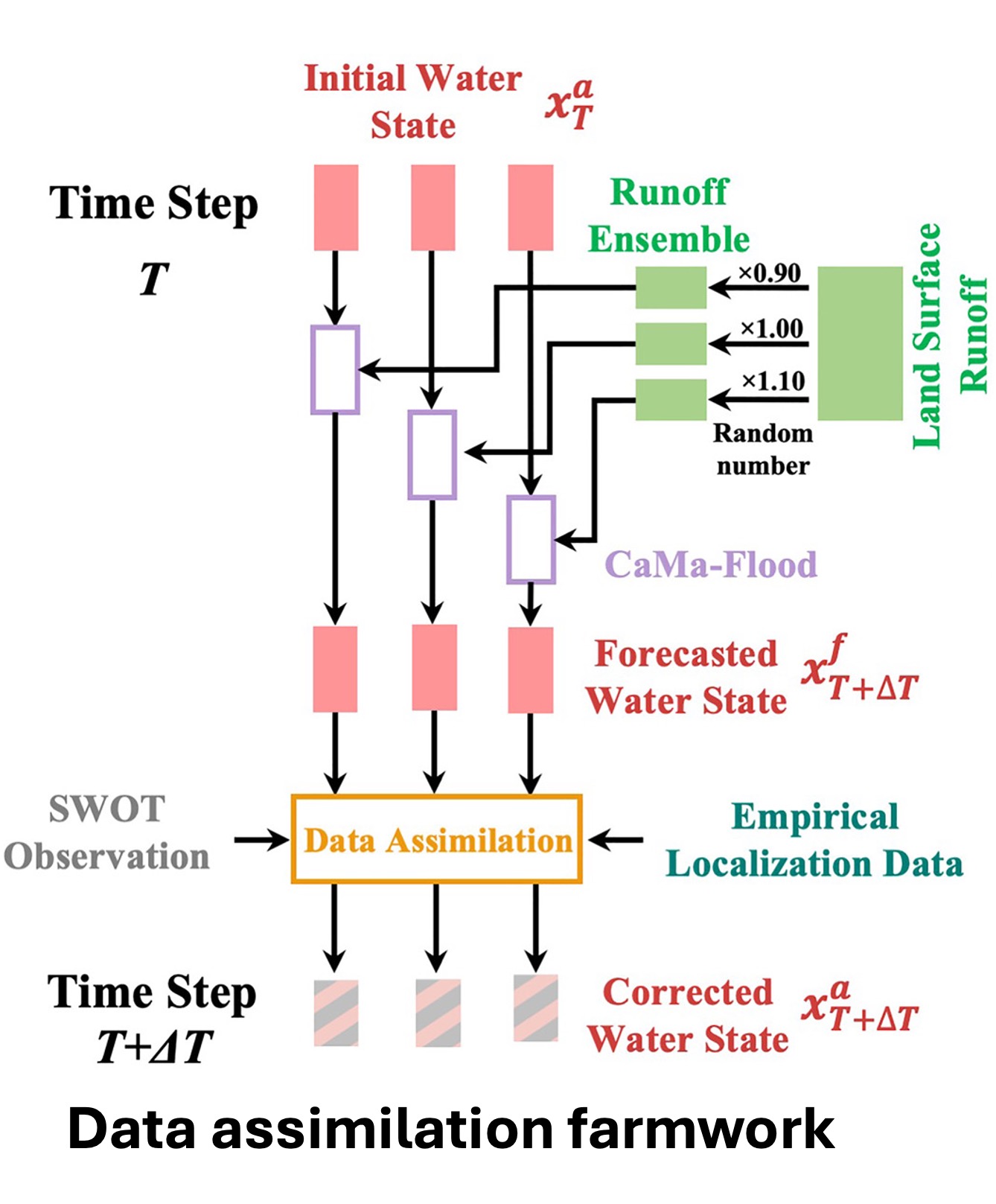
Data assimilation framework
We present a global-scale data assimilation framework designed for hydrodynamic modeling of river discharge in support of the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) satellite mission. Built around the CaMa-Flood hydrodynamic model, the framework is developed to estimate river discharge accurately at global scales while maintaining low computational demands. To enhance the use of observational data, we implement a physically-based adaptive empirical localization method, allowing the framework to incorporate a large volume of observations efficiently. Moreover, the framework may apply various data assimilation techniques, allowing hydrodynamic models to mature over time.
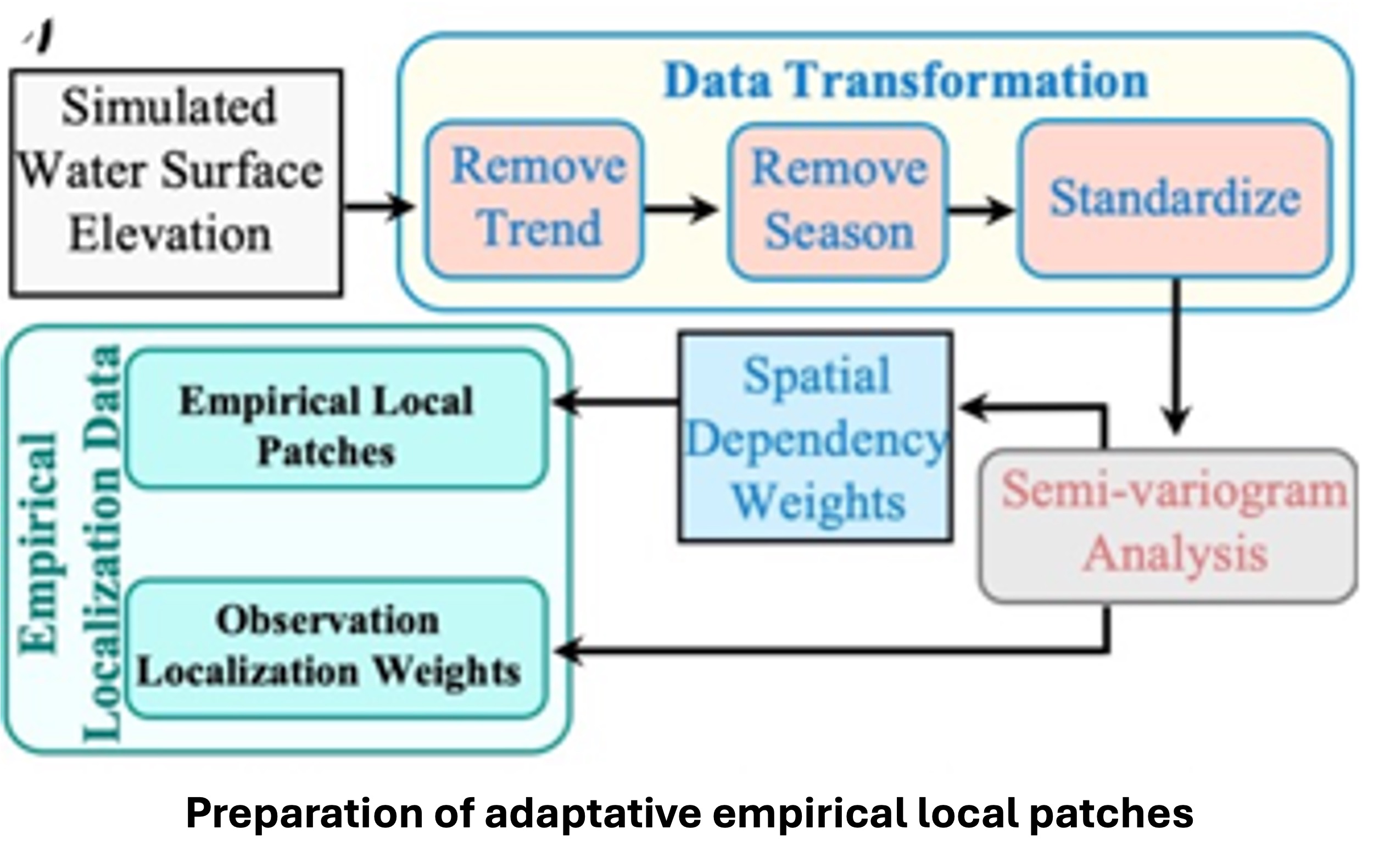
Empirical Local Patches for Data Assimilation
Empirical local patches identify relevant areas of a river system for specific locations based on water level behavior. Instead of assuming all nearby points influence each other equally, this method analyzes actual patterns in simulated water surface elevation to pinpoint strong relationships. By eliminating trends and seasonal variations, it focuses on meaningful spatial connections to create custom patches. These patches can change in size depending on the river’s characteristics; for example, the Amazon has a broader influence than a smaller stream. This approach enhances the accuracy of river models and satellite data for predicting water levels. This method better reflects the actual correlations of the river network, moving beyond simplistic distance assumptions. In summary, empirical local patches strengthen the selection of observations, improving the precision of hydrologic data assimilation.
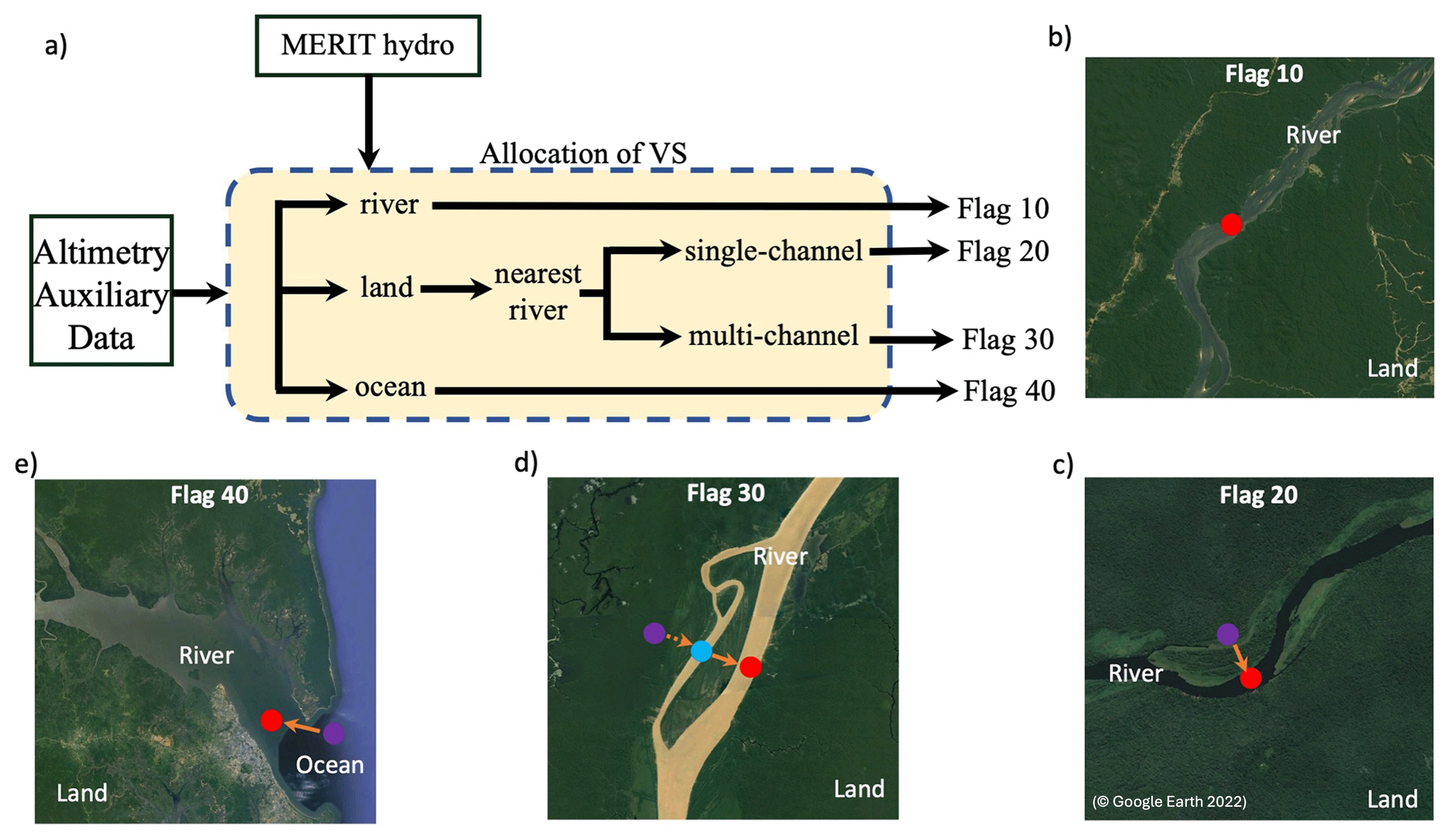
Altimetry Mapping Procedure for Global River Models
Satellite altimetry is an essential tool for monitoring river water levels and enhancing hydrodynamic models. However, linking satellite measurements, taken at specific points known as virtual stations (VSs), to river model grids can be difficult due to alignment issues. To address this, an Automated Altimetry Mapping Procedure was developed. This method automatically matches each virtual station (such as from the HydroWeb database) to the nearest location in the river network map (e.g., MERIT Hydro), factoring in land cover and river structure. Stations are categorized based on their proximity to rivers, including flags for those directly on rivers, on nearby land, or within complex features like multi-channel rivers or the ocean. By utilizing AltiMaP, researchers can more accurately identify suitable satellite points for model evaluation, reducing mapping errors and improving the connection between satellite data and model simulations. This method builds on the work of Revel et al. (2024) and is available for wider use in the hydrology community.
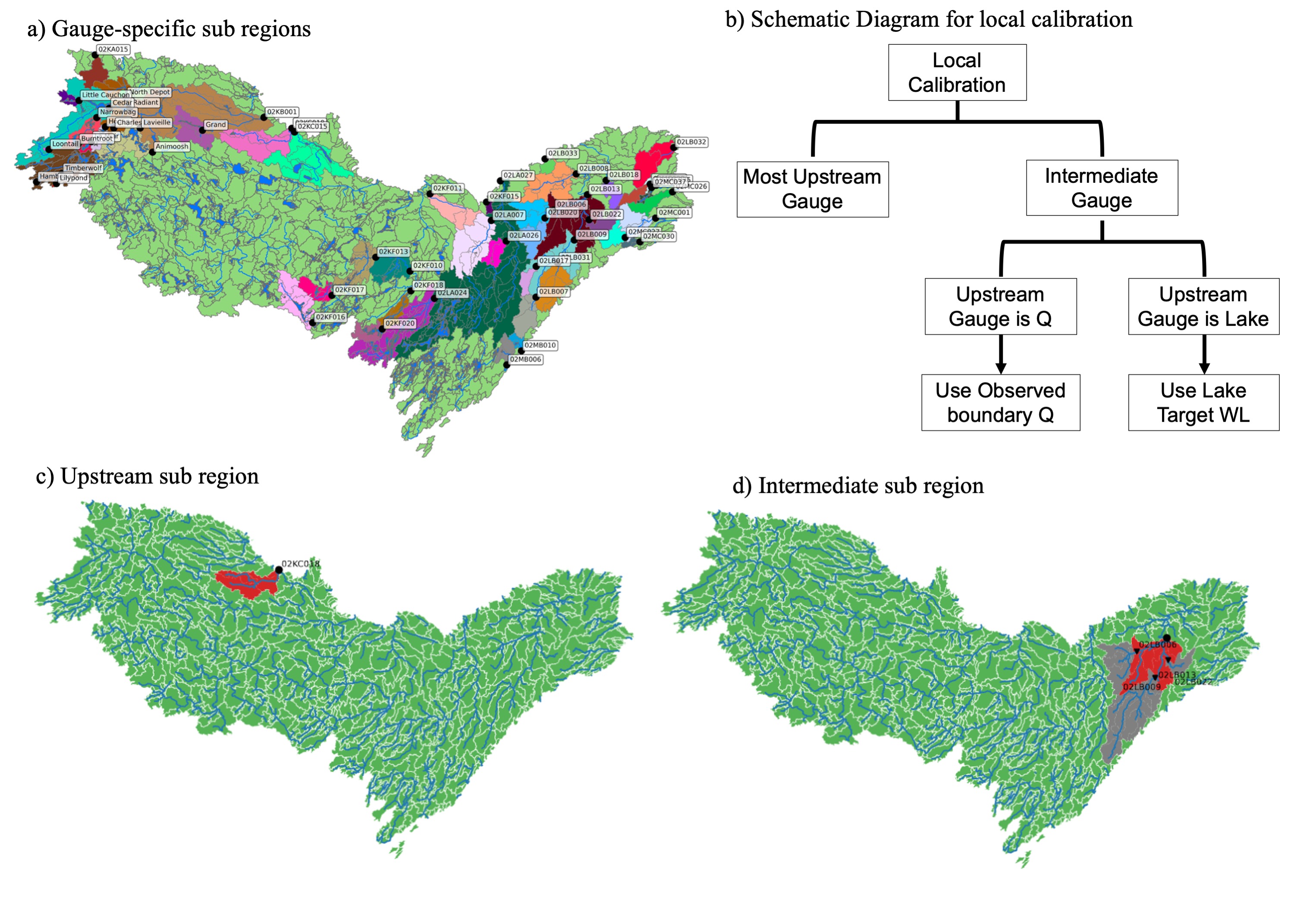
Local Calibration of River Routing Model
Accurate representation of surface hydrology is crucial in lake-dominated Canadian Shield watersheds. Spatial heterogeneity of conditions (e.g., soil, geology, terrain, vegetation, etc.) is highly influential in predicting accurate water dynamics. Since observations are sparse, calibrating the models locally is challenging. Therefore, different types of regionalization methods were used to transfer parameters to ungauged basins. These methods primarily depend on various physical characteristics of the watershed to identify similar catchments, which leads to reduced performance. To effectively address these limitations, we have developed a calibration strategy that precisely defines a subregion, strategically considering the river topology. We implemented this calibration strategy in the Ottawa River basin, located in southeastern Ontario, Canada.